Expert Overmolding Solutions - AMSL
What’s Overmolding?
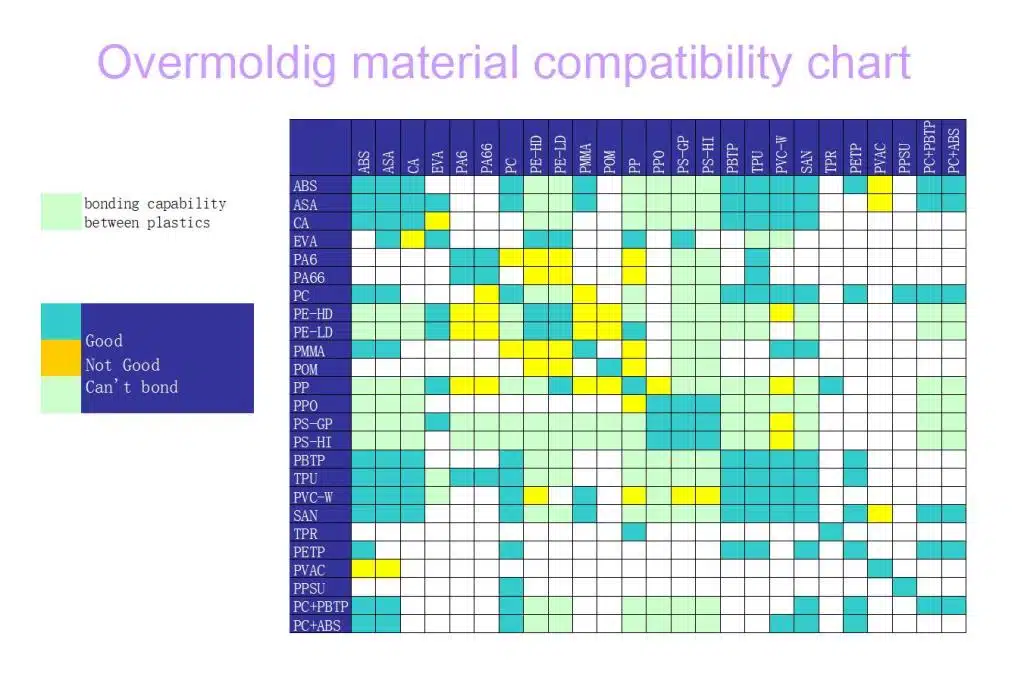
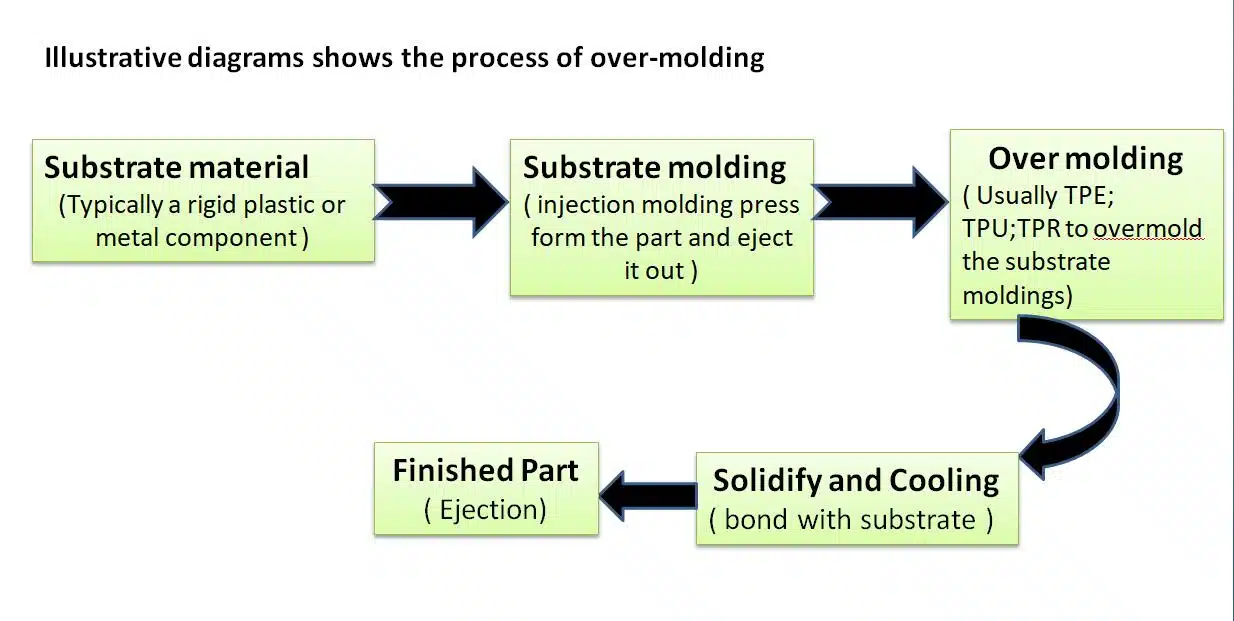
Overmolding also referred to as co-molding, is a manufacturing process similar to insert molding. It involves bonding a substrate material with a layer of rubber material to create a product. This technique chemical bond between two materials to achieve desired properties such as improved aesthetics, functionality, and durability.
Materials Selection
Substrate Materials: ABS, PP, PC, PA66-GF, etc.
Overmolding Materials: TPE, TPU, TPR.
Why Choose These Materials?
- Color Variety: Enhance the visual appeal of your products.
- Functionality: Increase the performance and features of your products.
The main reasons are get numerous colors and increase the functionality. For example the handles through overmolding design process, we can get a colorful and a “soft surface”.
What are the benefits for overmolding process?
Overmolding offers the creation of seamless, durable, and aesthetically across sectors such as consumer electronics, automotive, medical devices,tools, and sporting goods.
Enhanced Product Performance
such as abrasion resistance, anti-slip, impact and high-temperature resistance.
Improved Aesthetics
enhance the visual appeal of your products with multi-colors and texture finishes.
Reduced Assembly Costs
No need secondary process for assembly, reduced production costs
Improved user experience
By adding soft-touch or ergonomic features, the plastic parts can become more comfortable and user-friendly.
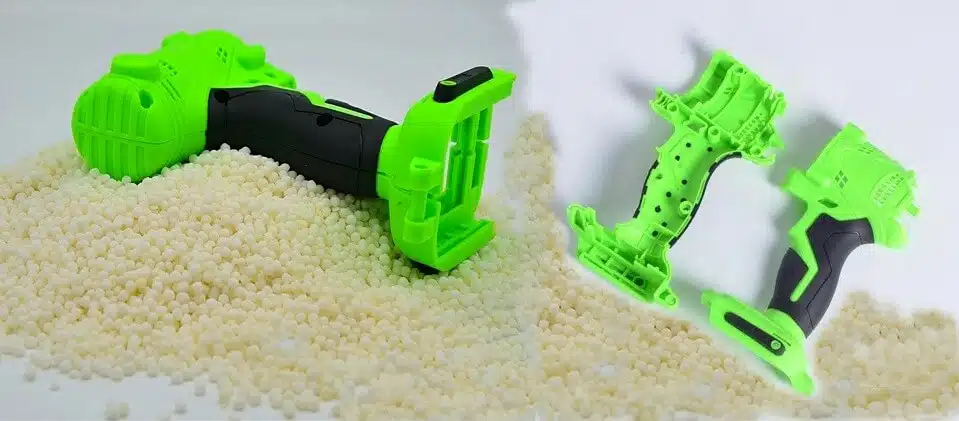

Overmolding vs. Double-Injection Molding
Overmolding (Co-Molding):
Operation: Involves two separate injection molding process. Initially mold the substrate part, then insert the initial molded parts into the second mold for overmolding
Quality: While capable of producing high-quality parts, but may have material bonding issues.
Cost: Compare to double-shot molding, overmolding requires 2 sets of standard molds and machine should be more cost-effective.
Design Complexity: Overmold design is generally less complex compared to double shot molds.
Production: It’s suitable for small volume production.
Double-color Molding (2-Shot injection):
Operation: Substrate and overmolding materials are molded on the same machine in two sequential injections, with the final overmolded part ejected only once. This process is performed on a 2-shot injection molding machine.
Quality: Known for producing high-quality, seamless parts with precise material alignment, making it ideal for intricate designs and tight tolerances.
Cost: Double-color molding tends to be more expensive as the need for specialized equipment and molds.
Design Complexity: Double shot mold design is significantly more intricate and requires advanced engineering expertise compared to overmold design.
Production:2-shot molding is suitable for large volume and mass production.
AMSL Overmold Design
Enhancing Product Durability and User Experience
At AMSL, we specialize in overmolding solutions tailored to the unique needs of various industries. Our projects are including:
✅Overmolding techniques for electronic enclosure design
✅Overmolding applications in medical device production
✅Cost-effective overmolding solutions for consumer product assembly
✅Overmolding process optimization for industrial equipment durability
We can provide custom overmolding services to meet your needs and specifications.
Essential Design Considerations for Overmolding
- Pulling Grooves and Parting Surfaces
- Purpose: Facilitates easy separation of the mold from the substrate.
- Specifications:
- Flat sealing surfaces should have pulling grooves of 1.2mm width.
- Complex sealing areas require grooves of 1.8mm width.
- Step Holes and Spigot Holes
- Purpose: Prevents material overflow and enhances bonding.
- Specifications:
- Use step holes for corners and elongated parts to ensure proper material distribution.
- Spigot holes should be spaced 20-30mm apart and positioned at least 1mm from edges.
- Bevel Angles and Sealing Surfaces
- Purpose: Ensures tight sealing and prevents adhesive issues.
- Specifications:
- Limit bevel angles to 45 degrees.
- Maintain sealing surface widths of at least 1.2mm.
- Counter-Buttons and Wall Thickness
- Purpose: Avoids adhesive sticking and ensures structural integrity.
- Specifications:
- Design counter-buttons for holes or slots deeper than 5mm.
- Target a wall thickness of 1.5mm, with a minimum of 1.0mm.
- Material Flow and Sealing Gap
- Purpose: Optimizes material flow and prevents defects like burrs.
- Specifications:
- Maintain a TPE flow length/product thickness ratio of less than 150:1.
- Ensure a sealing gap of more than 1.0mm.
- Mold Material and Structural Support
- Materials: H13 or 420H steel for the mold.
- Purpose: Provides durability and stability to the mold structure.
Specifications:
- Leave an extra 0.07-0.13mm space at the sealing position of the soft rubber.
- Support rigid plastic with steel, especially behind soft plastic areas.
- Temperature Management and Venting
- Purpose: Prevents melting of base materials and enhances mold release.
Specifications:
- Maintain at least a 20-degree temperature difference between materials.
- Set venting depth at 0.01mm for TPE overmolding.
- Runner Polishing and Texturing
- Purpose: Improves mold releasing and reduces sticking issues.
Specifications:
- Avoid polishing runners to enhance mold releasing.
- If the cavity side is sticky, consider adding spring inserts.
Practical Applications and Impact
By adhering to these design guidelines, engineers can significantly enhance the quality and reliability of overmolded products. Here are a few practical outcomes of following these considerations:
- Increased Durability: Properly designed molds and adequate material support ensure that the final products are robust and durable.
- Enhanced Aesthetic Appeal: Smooth finishes and precise color are achieved through controlled material flow and sealing.
- Cost Efficiency: Reducing material overflow and minimizing production errors leads to lower manufacturing costs and less waste.
In conclusion:
Overmolding offers numerous benefits, including improved product performance, aesthetics, and cost-efficiency. At AMSL, we provide expert overmolding solutions tailored to your unique needs. Contact us today to learn more about how our overmolding services can enhance your product designs.