Innovative Mold-Making: Shaping Precision and Excellence with AMSL”
Mold-making refers to the process of designing and manufacturing molds – tools used for creating parts with molding materials such as resin, plastic, or metal to get uniformity and high-precision components. AMSL, as a leader in mold-making capable for making molds for different resins.
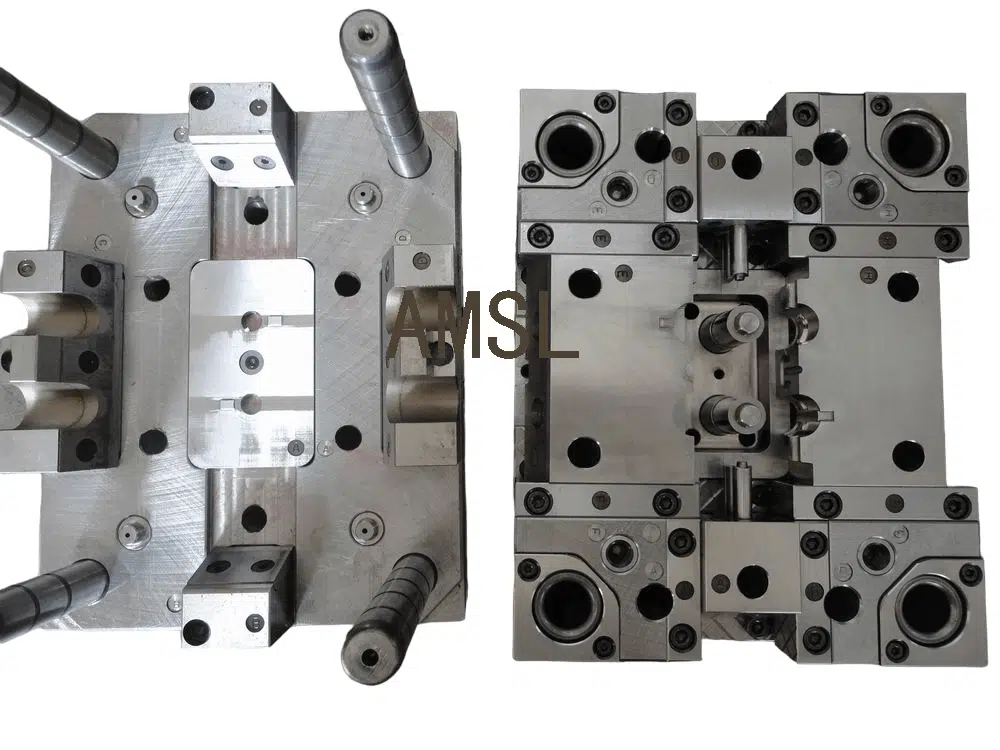
The Precision of Molds in Manufacturing 🏭
AMSL’s mould-making expertise ensures that every mold is engineered to produce parts with exact dimensions and tight tolerances. This precision is crucial for the assembly of complex products that require the highest level of accuracy.
Molds and the Power of Mass Production 📊
The true strength of molds lies in their ability to be used repeatedly, producing thousands to millions of parts. This capability makes molds a cornerstone of mass production, allowing industries to scale up efficiently.
Material Efficiency and Molds ♻️
With a focus on material efficiency, molds designed by AMSL minimize waste, making them crucial for both cost control and environmental sustainability. This efficiency is particularly evident in the use of thermoplastic resin, which are recyclable and adaptable to various applications.
Innovation Through Mold Design 💡
Innovative mold designs can lead to breakthroughs in product features and functionality. AMSL’s approach to mold-making fosters progress within the industry, helping clients stay ahead of the curve.
Quality Consistency via Molds 🔍
Consistency is key in manufacturing, and molds ensure that each part produced is a carbon copy of the last. This level of quality consistency is a hallmark of AMSL’s mold making services.
Speed of Production with Molds ⏱️
In today’s fast-paced market, speed is of the essence. Molding processes, such as injection molding and blow molding, allow for rapid production, enabling quick fulfillment of market demands.
Types of Molds for Different Resin and Their Applications
In mold-making process, we categorize mold types into two sections based on the different resins and processes used.
Based on Molding Material:
Thermosetting Plastic Mold:
- Chemical properties change permanently when cured.
- Not recyclable.
- Low production efficiency, but high heat resistance and strong rigidity.
Thermoplastic Mold:
- Physical state changes are reversible with heating and cooling.
- Recyclable.
- High production efficiency, lower heat resistance, and weaker rigidity compared to thermosets.
thermoplastic-injection-molding-for automotive- component
Difference Between Thermosetting And Thermoplastic
| Thermosetting | Thermoplastic |
|---|---|
| Chemical Properties | Physical Properties |
| Not Recycle | Recyclable |
| Intermittently Processing | Continuous Processing |
| Low Production Efficiency | High Production Efficiency |
| High Heat Resistance | Low Heat Resistance |
| Strong Rigidity | Weak Rigidity |
Based on the molding process
Injection Molding Mold:
- Ideal for thermoplastics, it is widely used for a variety of consumer and industrial products.
- High precision and suitable for complex shapes.
- Including 3C products (such as computers, communication devices, and consumer electronics), automotive and motorcycle structural parts, interior components, daily necessities, children’s toys, PVC water pipe joints used in construction, handles for different tools, precision instrument parts, etc.
Compression Molding Mold:
- Used for thermosetting plastics, such as rubber and silicone products.
- Suitable for large, fairly simple parts.
Such as various waterproof rings, trim parts, buffer parts, gaskets, mobile phone buttons, etc.
Plastic Extrusion Mold:
- Produces continuous shapes (e.g., pipes, rods, profiles).
- Suitable for long production runs of uniform cross-sectional parts.
- Mainly various profiles, such as aluminum alloy doors and windows for construction, wire ducts, pipes, rods, Processing of special-shaped materials, etc
Plastic Blow Molding Mold:
- Creates hollow plastic containers.
- Utilizes air pressure to form the shape within the mold.
- (such as various beverage bottles, plastic pots, cosmetic boxes, shampoo bottles, inflatable toys, daily chemical products, and other packaging containers)
Plastic Blister Molding Mold:
- Shapes simple plastic products through vacuum or pressure forming.
- Commonly used for packaging.
- Such as daily necessities, food, and toy packaging products
High-expanded Polystyrene Molding Mold:
- Forms foam plastic packaging materials using expandable polystyrene.
- Typically,for the protective packaging .
AMSL’s Mastering | Mold Making for Resin Casting
AMSL specializes in plastic injection molding, a method that leverages the durability of aluminum or steel molds to produce parts from a range of plastics. This process is the backbone of creating custom parts for various industries, highlighting the versatility of molds.
Mould Types for Resin Casting
High-Performance Unscrewing Molds
Threaded plastic parts are in high demand, and AMSL’s high-speed, precision-engineered unscrewing molds ensure the production of these components is both efficient and economical.
The MUD System: Quick Change Inserts
The MUD (Master Unit Die) System is another example of AMSL’s innovation in mold making. This system revolutionizes the injection molding process with its quick die change capability, offering unmatched operational flexibility.
The Art of 2 Shot Molds
AMSL’s 2 shot molds represent the pinnacle of mold making for multi-material and multi-color parts, enhancing product aesthetics and functionality while optimizing the molding cycle.
Metal-Inserted Injection Molds
Combining the insulating properties of resin with the electrical conductivity of metal, metal-inserted injection molds cater to a niche in electronic components, demonstrating the innovative use of molds in manufacturing.
The Efficiency of Hot-Runner Molds
For large or intricately designed products, AMSL’s hot-runner molds optimize the injection molding process, ensuring high-quality output and reduced waste.
Metal Casting Mold
Precision Die Casting Molds
Die casting molds from AMSL are perfect for creating precise parts from metal alloys, where strength and accuracy are paramount. This process underscores the versatility of mold making beyond plastics.
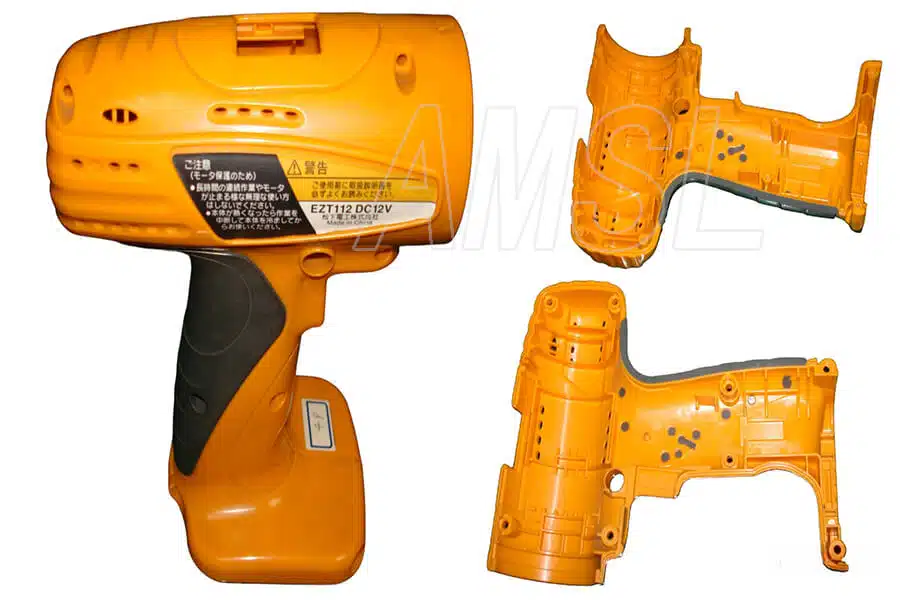
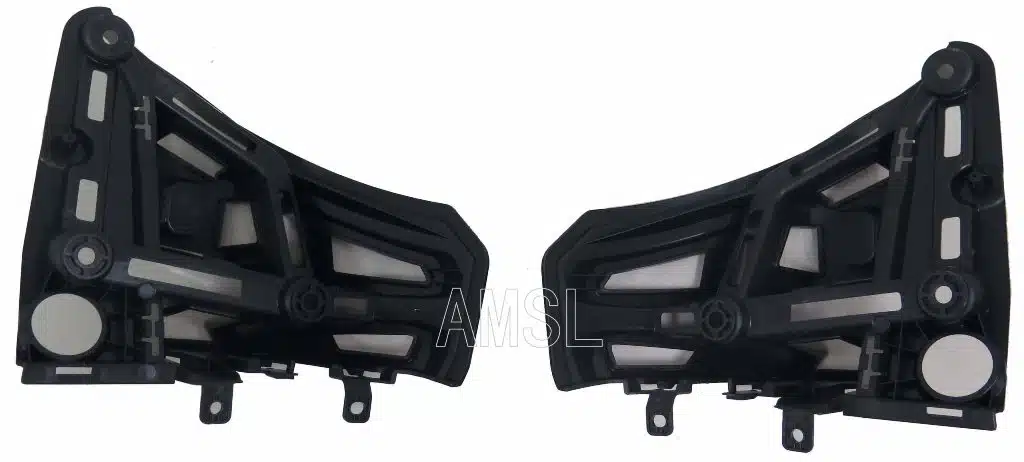
Here are some of our projects we made:
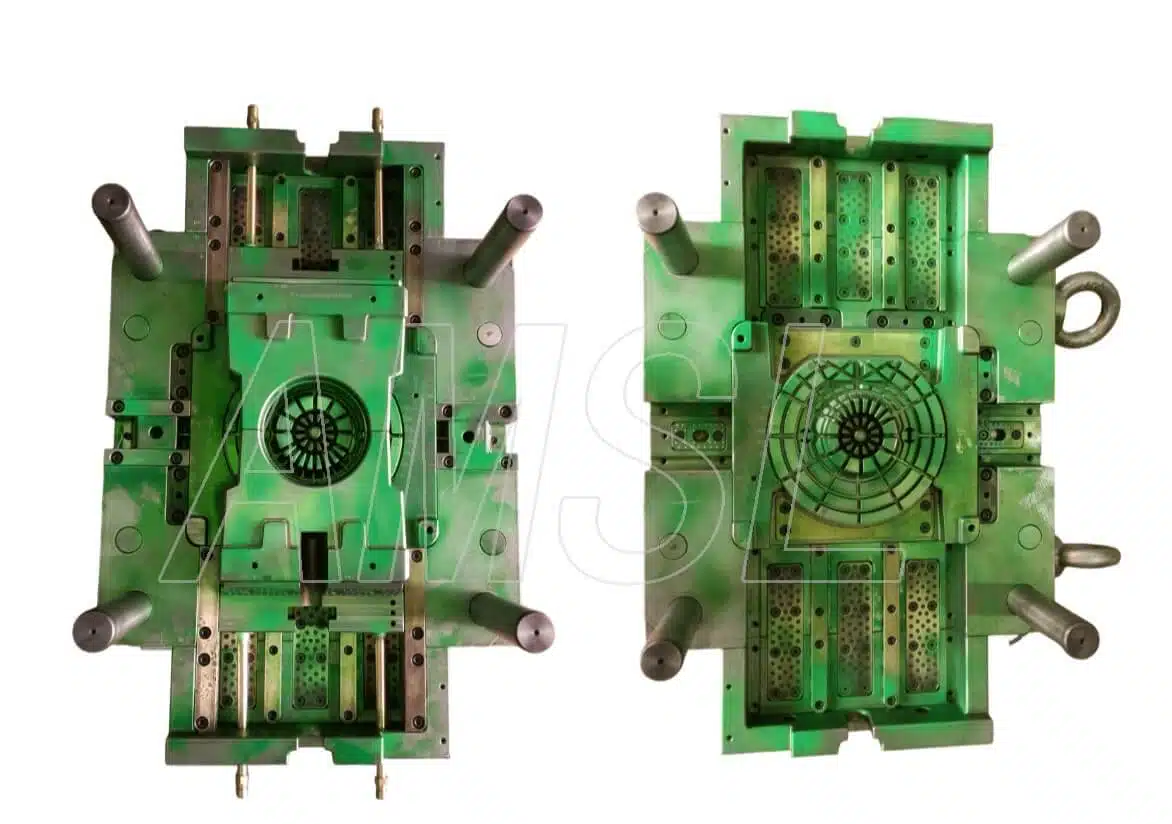
Standard Injection Mold
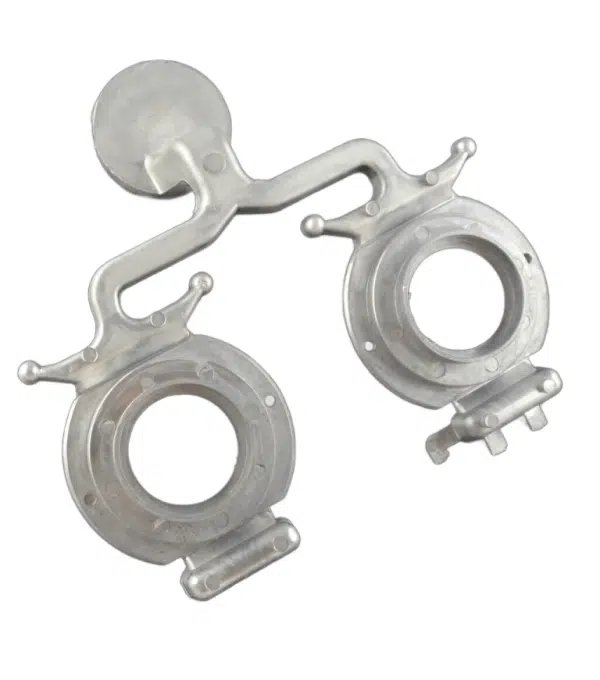

Metal Castings
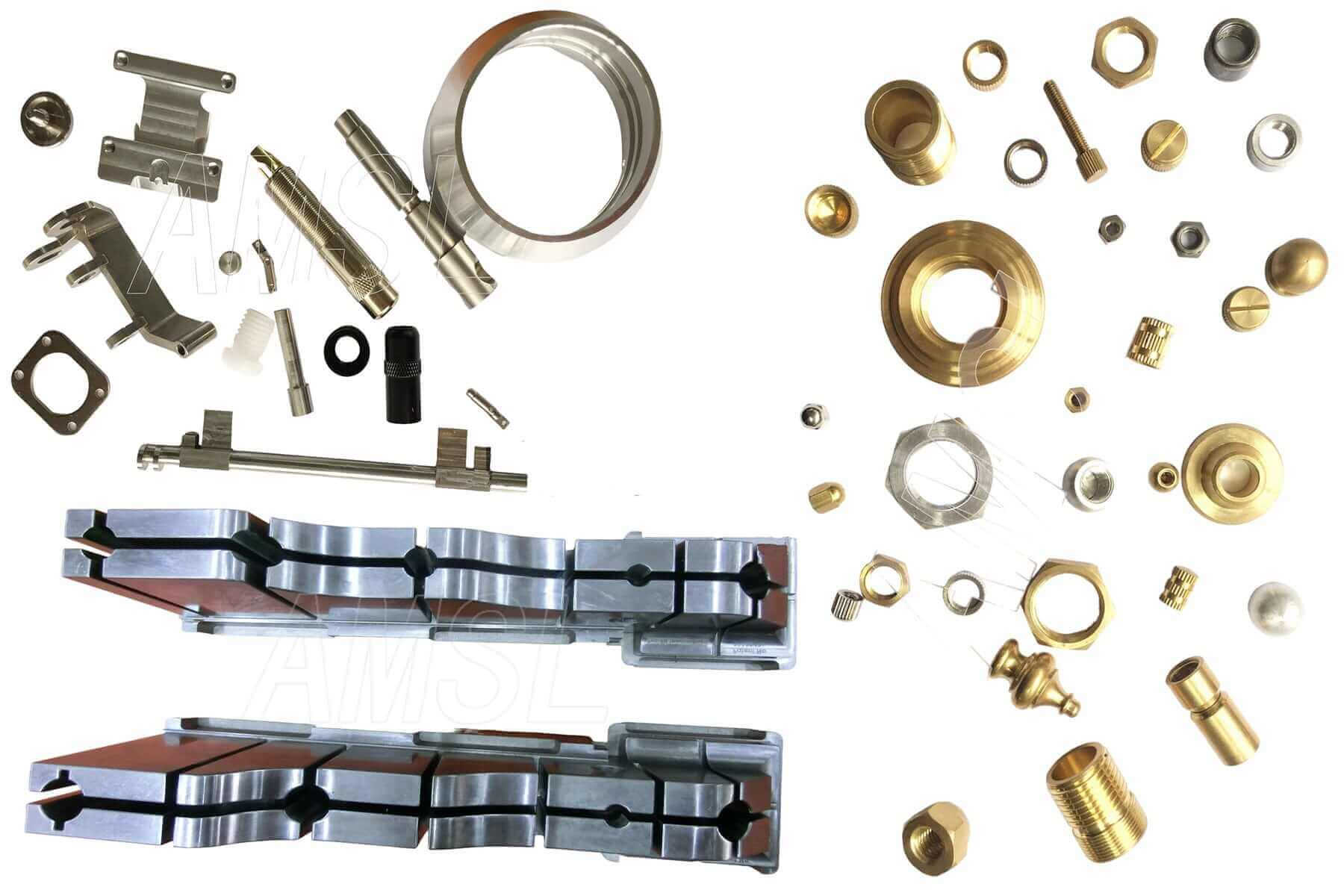

CNC Machinings
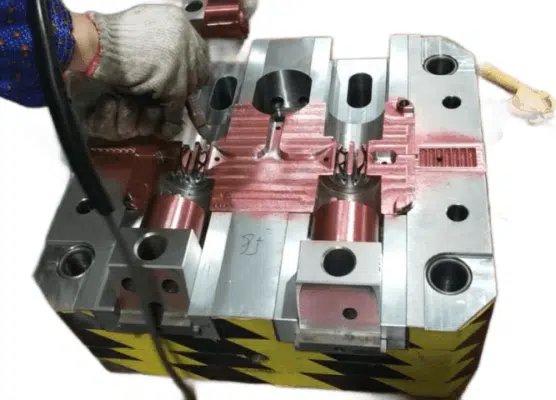
Die Casting
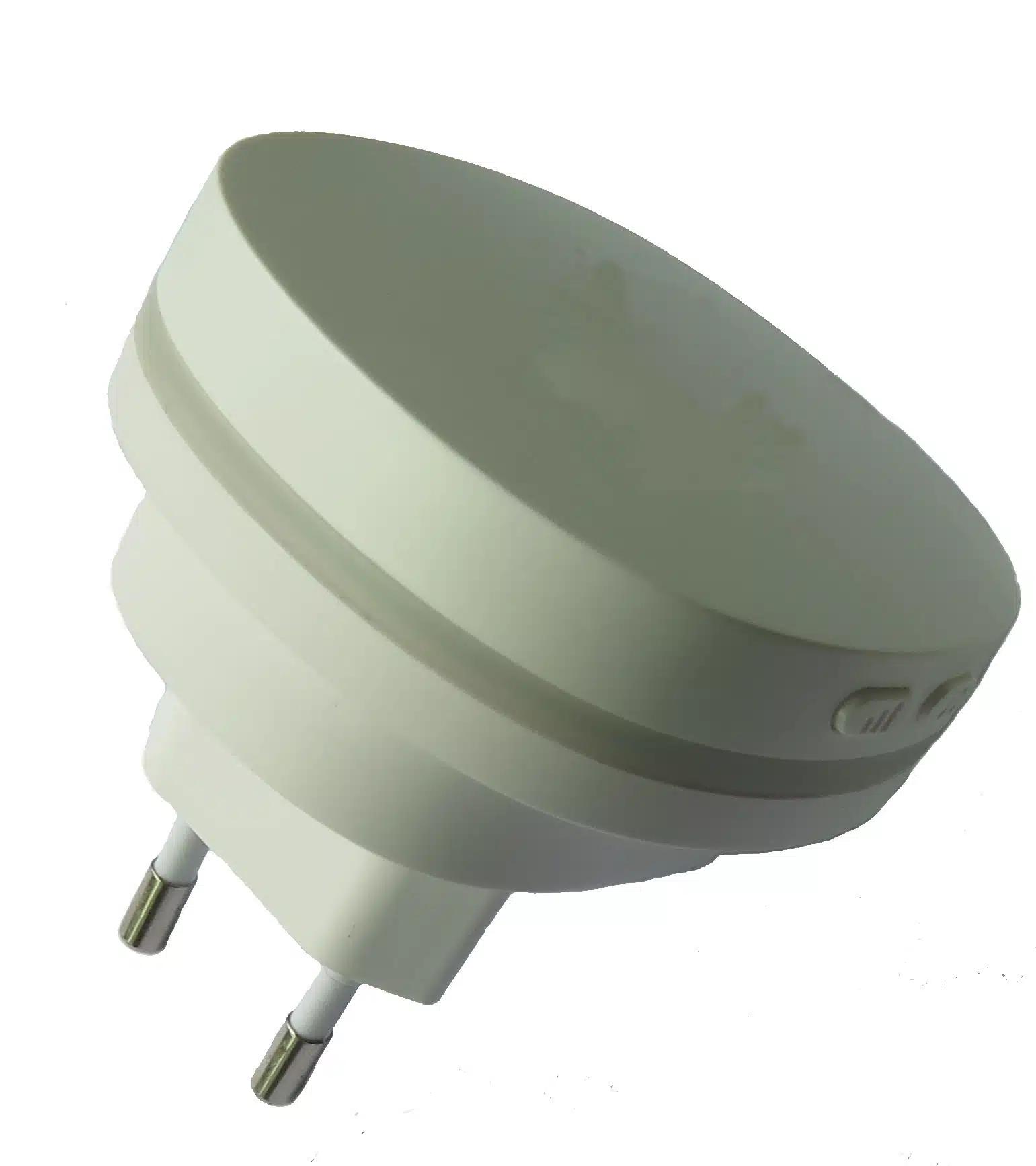

insert molding
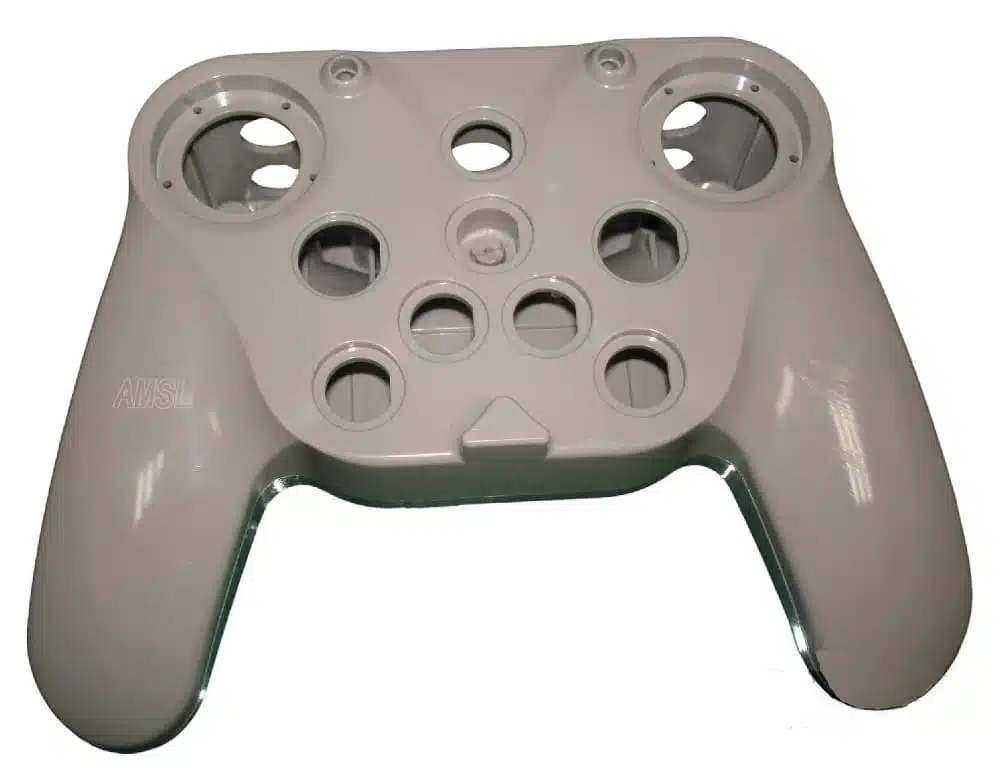

Electronic Component
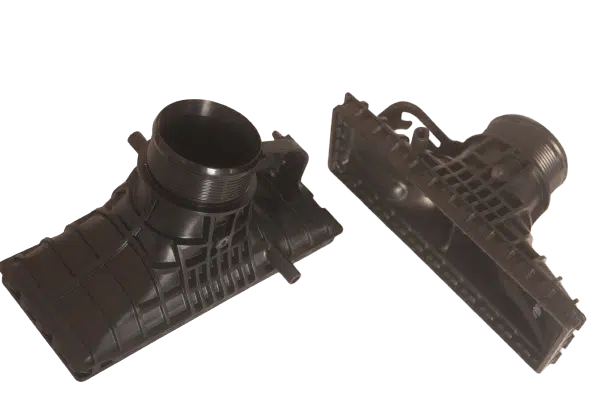

Automotive Components


